Using an on-demand, multi-sensor wearable 3D-printed medical device for hemodialysis patient care

- ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGIES
- Text & Image
- August 20,2020
Recently, Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has been widely used in various applications. As part of the ICT application, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analysis has become core technologies in various industries. ICT can be applied in the eHealth industry, including healthcare, disease management, public health, and genetic test. Moreover, ICT can be used in advancing vehicle structures and transportation infrastructures, which gives rise to Smart Transportation that provides safer and more comfortable transporting experience.
ICT has become the key developing field as it is related to smart manufacturing. Therefore, governments around the world are developing the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0), which includes the application of human-robot collaboration, remote monitoring, and smart tools. In 2020, the world is strongly hit by the pandemic, which inspires more businesses and industries to develop non-human factories or a more flexible business model that can increase operation efficiently and quality.
Industry 4.0 – International Trend of Smart Industry
In Germany and the US, the development of the Smart Industry is mostly lead by corporates and emphasizes on industry-academia collaboration to nurture professional talents. With regard to development, Germany focuses on cloud computing, smart grid, and big data analysis; on the other hand, the US focuses on the development of advanced materials, informatics, and digital technology to face energy and resources problems in the future.
As for countries in East Asia, Japan has noticed the importance of computer integrated manufacturing and the innovation of automatic factories since the 1980s. In the future, Japan will focus more on the development of AI and Internet of Things. Meanwhile, Korea’s strategy is to reinforce its strength in the manufacturing industry and combine with ICT to reach the goal of raising productivity and reducing industrial costs.
Foundation for Smart Industry – the R&D of Computer Sciences and AI
The foundation of the Smart Industry includes cloud computing, big data, AI, and other technology in the field of computer sciences. Comparing Taiwan’s R&D competitiveness in computer sciences with other countries, Taiwan ranks no. 14 on the number of publications in computer sciences among 221 countries (fig.1). Meanwhile, the published documents were cited for 56,639 times, which is about 7 times of the number of publications (8,324 pieces). Taking a closer look at the field of AI technology, Taiwan ranks no.15 on the number of publications and was cited 21,598 times in other papers. The data above shows that Taiwan’s R&D in computer sciences and AI technology has a certain impact among the international research community.
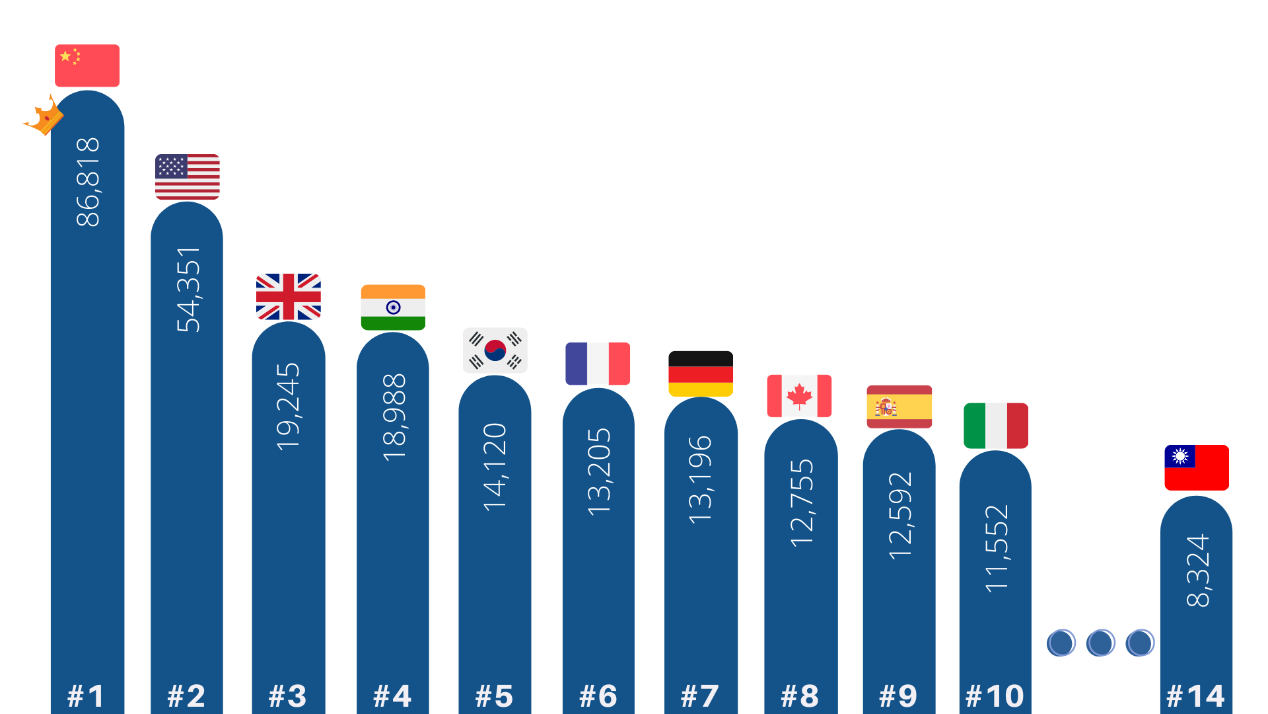
Fig 1. Global computer sciences paper publication amount from 2014 to 2019. Resources: InCites™ Journal Citation Reports™
Focusing on the outcome of Taiwan’s research institutions’ contribution in computer sciences, interdisciplinary applications, and AI from 2014 to 2019 (Table 1), NTU has the highest amount of journal publications (1054 pieces), followed by NCTU (862 pieces) and NCKU (834 pieces). As for the percentage of papers that have been cited, NTUST ranks the first with 65.01% of papers being cited, NCTU ranks the second (62.88%), and NTU ranks the third (62.43%). It is noticeable that more than a quarter of the publications from NTU, NCTU, NTUST, and NTHU are results of international collaboration. The results show that Taiwan, with the country’s strong research capability, has been actively involved in various international research programs.
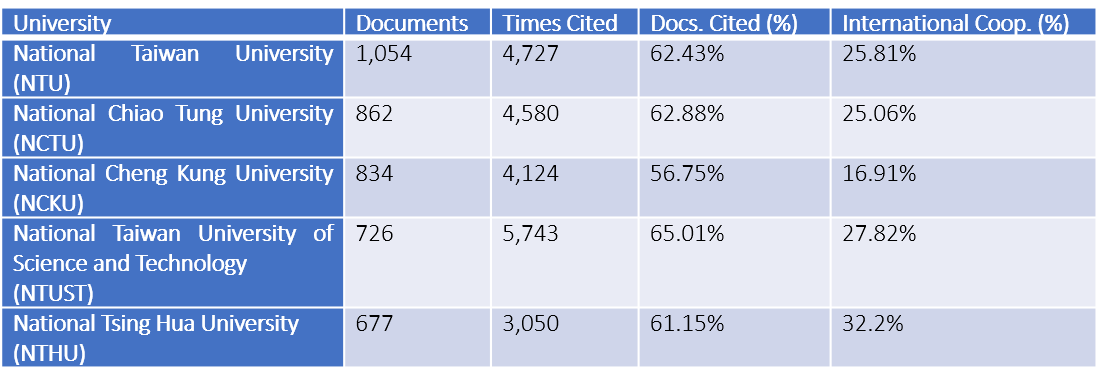
Table 1. Taiwan’s top five institutions in computer sciences interdisciplinary applications and AI from 2014-2019, sorted by publication amount. Resources: InCites™ Journal Citation Reports™
To understand Taiwan’s research institutes’ performance in comparison with other Asian countries, the data of Japan’s research performance in the same field were extracted (Table 2). From 2014 to 2019, the University of Tokyo published 1819 pieces of papers, Osaka University published 992 pieces, and Kyoto University published 877 pieces. The number shows that Taiwan published fewer papers than Japan did in the past five years, however, it can be seen that Taiwan has a higher rate of papers being cited. This indicates that although the number of publications in Taiwan is lower than Japan, the quality and impact of these papers are still noticeable.
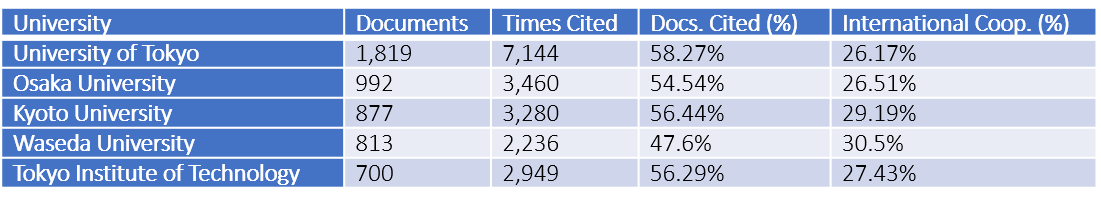
Table 2. Japan’s top five institutions in computer sciences interdisciplinary applications and AI from 2014-2019, sorted by publication amount. Resources: InCites™ Journal Citation Reports™
Smart Country – Taiwan’s Digital Transformation Strategies
Despite starting off late in the development of Industry 4.0, Taiwan has set solid foundations for the smart capitalization with the country’s strength in AI and information technology and the government’s support on cultivating talents. In 2017, Taiwan’s government activate the “DIGI+ Strategy” and “The 5+2 Industrial Transformation Plan” to accelerate digital transformation and the development of the Smart Industry. Meanwhile, the government also announced the “AI Taiwan Action Plan” under the “DIGI+ Strategy” to further develop R&D in AI technology and encourage industry-academia collaboration in the development of the Smart Industry. Taiwan’s government aims to gain opportunities and advantages when facing the fourth industrial revolution, the trend of Industry 4.0.
STAY CONNECTED. SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER.
Add your information below to receive daily updates.