The Third Generation Semiconductors: The Rise of SiC Power Semiconductor Devices

Author(s)
Hsi-Yin Yeh & Ming-Yi LinBiography
Hsi-Yin Yeh, PhD., Associate Researcher, Science & Technology Policy Research and Information Center, National Applied Research Laboratories (Corresponding Author, email: hyyeh@narlabs.org.tw)
Ming-Yi Lin, PhD., Assistant Researcher, Science & Technology Policy Research and Information Center, National Applied Research Laboratories
Academy/University/Organization
National Applied Research Laboratories-
TAGS
-
Share this article
You are free to share this article under the Attribution 4.0 International license
- ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGIES
- Text & Image
- January 02,2022
The aerospace and satellite technology has been a worldwide focus in recent years. As SIA’s 2021 State of Satellite Industry Report indicates, the global space and satellite industry revenue has reached 371 billion USD in 2020, and the satellite industry is the dominant sector with 271 billion USD in revenue. The satellite industry contains four major sub-sectors: satellite manufacturing, launch industry, ground equipment, and satellite services. The revenue is mainly contributed by ground equipment (50%, 131.5 billion USD) and satellite services (44%, 117.9 billion USD). In addition, the number of satellites launched in 2020 has tripled compared to the year before. At the end of 2020, there were 3,371 satellites orbiting the earth, showing an increase of 37% in 2020. Moreover, as 2021 marks the beginning of low earth satellites being used for mobile communications, mobile communication and satellite communication were no longer considered two independent industries. The satellite market value is expected to rise to 295 billion USD in 2022, with an annual growth of 3.3%. The numbers all suggest a fiercer global competition for satellite technology in the near future.
There is a wide range of applications for satellites. The weather satellites can help the meteorologists with weather forecasts; the military satellites can gather intelligence from high-tech electronics and high-resolution photography; the earth observation satellites can monitor the temperature, weather and environment. The most well-known application for satellites is to provide global positioning services (GPS) and serve as relays for television, phone, radio and internet. Recently, telecommunication service providers have also succeeded in transmitting 4G data to the ground using low earth satellites. This will complement the ground communication and serve as a possible backup for special ground communication in an emergency, such as disaster or war time communication. These applications are critical for future communication and will bring huge changes to our life.
Global Aerospace and Satellite Technology R&D Analysis
We first looked into the global publication trend in satellite technology in the recent 5 years on Web of Science (Clarivate) to peek into the R&D capabilities of major countries in the field. There is a total of 23,666 publications between 2017 and 2021 worldwide. Top three countries in terms of publication quantity are China (5,005 papers), USA (3,697 papers), and Germany (1,185 papers). Taiwan is ranked 22nd in the 157 countries, with 169 papers total. China and USA are obvious leaders in the field during 2017-2021 (See Figure 1), and the number of publications of Taiwan is holding steady, at around 33 per year.
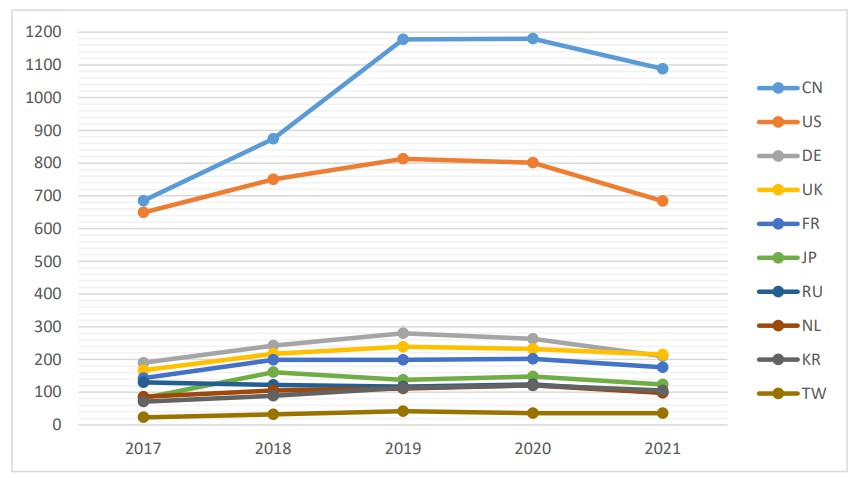
Figure 1 : Publication trends in Aerospace and Satellite technology for major countries, 2017-2021 (Data Source: Web of Science)
If we further compare the publication indicators between Taiwan and major countries, we will find that, albeit fewer in number, Taiwan’s relative impact factor (2.23) is higher than world average, and the percentage of high-quality papers for Taiwan is also high (13.61%). These suggest that Taiwan performs well in research in the field of aerospace and satellite (See Table 1). On the other hand, the analysis of collaborations shows that the percentage of international collaboration is pretty high in Taiwan (64.5%), but the collaboration with the industry is lower (1.78%).
Table 1: Publication indicators for major countries in Aerospace and Satellite field, 2017-2021
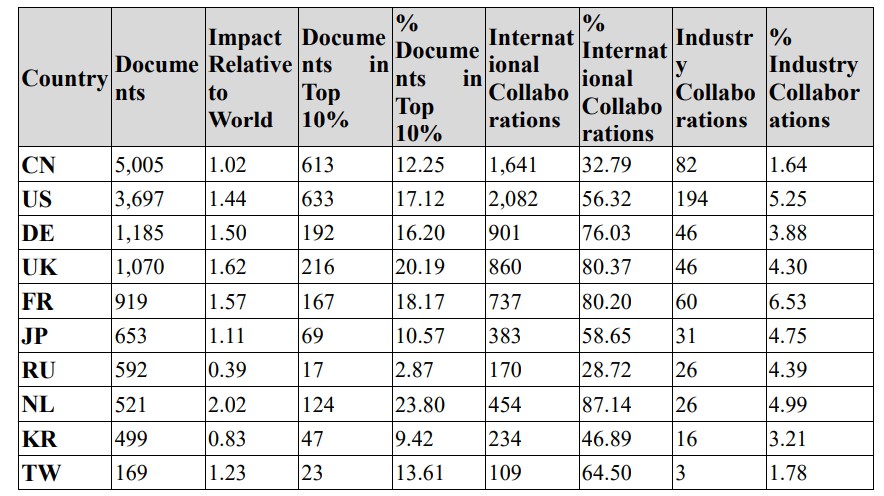
(Data Source: Incite)
The deep space mission of the National Central University is a great demonstration of Taiwan’s academia efforts in aerospace and satellite technology. The mission aims to bring scientific payloads to the moon in 2023, to conduct measurements of earth-moon deep space radiation environment, and to validate payload experiments. At the same time, with the support of the National Space Organization via its cube satellite project, the National Central University has successfully conducted scientific observations in the ionosphere. This is done by IDEASSat, the very first satellite designed, developed and tested by a Taiwanese team. The satellite was launched by SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket in January of 2021. It was equipped with a “Made in Taiwan” high-resolution remote optical CMOS image sensor. This is a critical step to establish Taiwan’s capability in designing and developing key components for remote image sensing payloads.
Current State of Aerospace and Satellite Industry in Taiwan
With the growing revenue of the global space industry, companies across the globe, including those Taiwan, are all eyeing space industry as the next high-growth opportunity. Lower costs of launch, private investments, and future high-value commercial applications such as satellite broadband or space tourism are all factors pushing the market surge. Amongst all applications, satellite broadband is projected to be the one with the most potential. Morgan Stanley believes the next key driving factors of space industry is mass production and lower costs of satellites. Interesting enough, Taiwan is known for its ability to reduce production costs, which led SpaceX to outsource its ground equipment manufacture to Taiwan.
Currently, the space industry in Taiwan mostly focuses on ground equipment manufacturing, including antenna, communication modules and power supply components, etc. But the recently emerging market of small/micro- and nano-satellites (under 500kg) represents a good opportunity for Taiwan’s companies to step up their game. Compared to the long-term investment, complicated design and expensive costs required for traditional satellites, the short life cycle and relatively low price tags of small satellites offer an opportunity for a new business model similar to consumer electronics. This means motives and advantages for Taiwan’s electronic industry. From compound semiconductor, chips, modules to system, there are already hundreds of Taiwanese companies in the space industry supply chain. In recent years, startups are also joining the game. Tron Future Tech and Tensor Tech are two startups to watch. They have developed innovative key satellite components: ultra-thin radar and light-weight spherical motor, and have received orders from National Space Organization and companies overseas. Taiwan has been more aggressively investing in aerospace area in recent years. In addition to the billion NTD annual budget for National Space Organization, the government plans to allocate 25.1 billion NTD in the next 10 years to foster the industry. As the famous quote from Star Trek puts, “Space: the final frontier”, in the new territory, hopefully Taiwan will rise and quickly find its place.
References
- 1State of the Satellite Industry Report (2021), Satellite Industry Association, https://sia.org/news-resources/state-of-the-satellite-industry-report/
- Taoyuan City Government cooperated with National Central University to development the aerospace industry (2021),Central News Agency ,Retrieved from: https://www.cna.com.tw/news/ahel/202109060227.aspx
- Beyond SpaceX: Why Taiwan’s Space Industry Is Attracting American,Retrieved from: VCshttps://techtaiwan.com/20210830/taiwan-beyond-spacex/
- Booming of Small Satellites, Huge Change in the Ecosystem of Space Industry,Retrieved from: https://news.pts.org.tw/article/510839
- Small Satellites Represents an Catch-up Opportunity for Taiwan’s Space Technology,Retrieved from: https://www.bnext.com.tw/article/52531/planet-labs-cubesat-nasa
- Space Industry Competition, Are There Opportunities for Taiwan’s Startups?,Retrieved from: https://meet.bnext.com.tw/articles/view/47789?
- Space: Investing in the Final Frontier,Retrieved from: https://www.morganstanley.com/ideas/investing-in-space
STAY CONNECTED. SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER.
Add your information below to receive daily updates.