The Capturer of Sea Wind Characteristics-the Triton Satellite

Author(s)
Hung-Yu KaoBiography
Hung-Yu Kao received his PhD degree from the Electrical Engineering Department, National Taiwan University in 2003. He is currently a professor of the Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering (CSIE) of National Cheng Kung University. He is also the chair of the IEEE CIS Tainan Chapter. His research interests include Natural Language Processing (NLP), Web information retrieval / extraction, knowledge management, data mining, social network analysis and bioinformatics. He has published more than 100 research papers in refereed international journals and conference proceedings.
Academy/University/Organization
National Cheng Kung University-
TAGS
-
Share this article
You are free to share this article under the Attribution 4.0 International license
- ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGIES
- Text & Image
- February 20,2021
Epidemic diseases are a big challenge for today's densely populated cities. Due to the high density of disease exposure, once new diseases and epidemic diseases cause small-scale infection clusters, they are very likely to cause large-scale infections in a short period of time. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic endangered people’s health and national security, and severely damaged industries and the economy. Public health is indeed an issue that we must now face and deploy in advance. It will also be an important issue to involve technological epidemic prevention to assist or even lead decision-making.
The integrated research team of National Cheng Kung University that combines researchers from computer science and information engineering, statistics, nursing and hospitals integrated health and epidemic information to build a heterogeneous medical and epidemic platform. This platform provides intelligent computational functions and social network modeling to utilize the country's overall medical information for constructing real-time applications. We focused on three parts, i.e., the medical data-assisted platform, real-time medical data analysis and patient tracking, urban epidemic prevention, and real-time decision support for monitoring and early warning.
With the changes in human settlement behaviors, people tend to migrate to cities, and the development of large cities has created many public health challenges that have not been faced in the past. This challenges the decision-making ability of urban administrative authorities. "Public health and health care" is one of the most important but also among the most challenging applications in the development of smart cities. During 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic endangered people’s health and national security, and severely damaged industries and the economy. Public health is indeed an issue that we must now face and deploy in advance. It will also be an important issue to involve technological epidemic prevention to assist or even lead decision-making.
Whenever any epidemic disease enters the stage of community infection and cluster infection in a hospital, hospitals are the last-line fortress of epidemic disease prevention. To prevent the expansion of cluster infections in hospitals, it is especially important to start tracking patients' contacts early. The trajectory of human movement and the chance of contact with potentially COVID-19 infected persons are important keys to causing community infection and hospital cluster infection. So far, we have not been able to effectively assist in tracking crowd contacts and indoor trajectory changes while maintaining personal privacy.
The research team in National Cheng Kung University combines computer science and information engineering, statistics, nursing and hospital teams to use the development results of the three-year integration projects and integrate more health and epidemic information to build a heterogeneous medical and epidemic platform. This platform provides intelligent computational functions and social network modeling to utilize the country's overall medical information for constructing real-time applications. We have integrated our previous research results and focused on three parts, i.e., the medical data-assisted platform, real-time medical data analysis and patient tracking, urban epidemic prevention, and real-time decision support for monitoring and early warning.
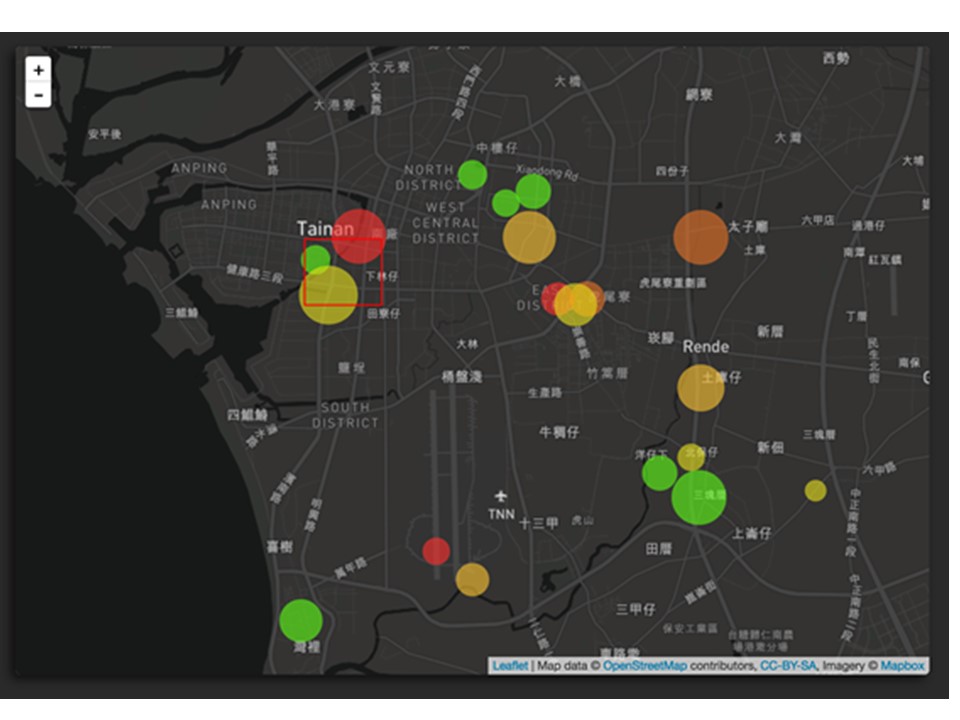
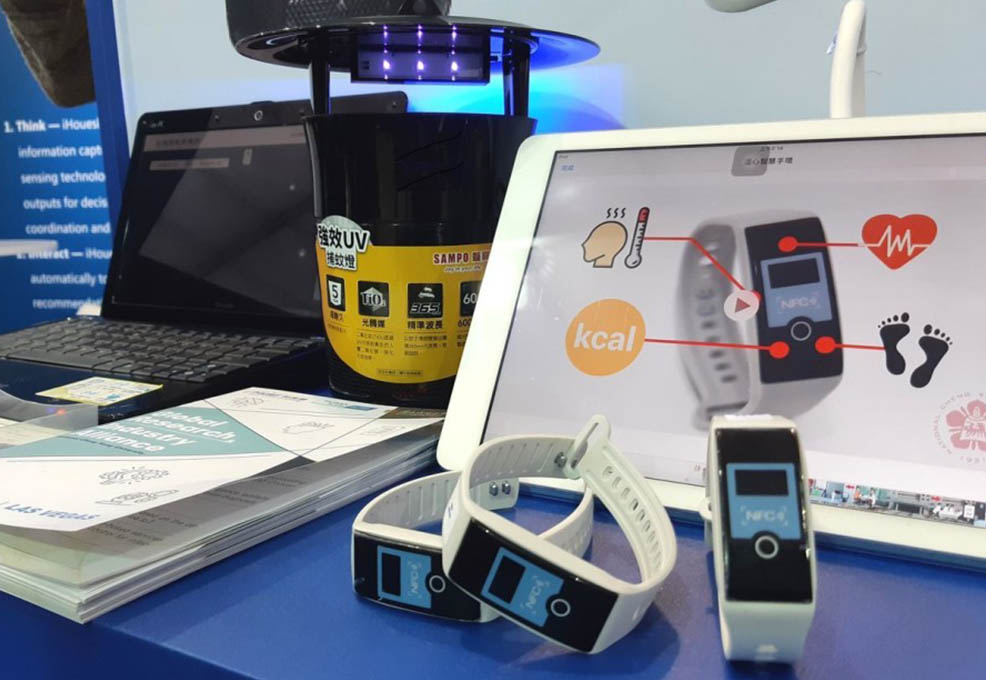
Figure1: IoT mosquito map
In this integrated system, we use IoT techniques combined with public health detection devices to implement effective health and environmental data value-added applications, as shown in the Figure 1 and Figure 2. We built this epidemic prevention data integration platform based on the statistical data of mosquito traps and vector mosquitoes. At present, we will first combine the user's body temperature obtained by the body temperature bracelet, and then combine the basic and environmental information provided by various hospitals to construct this epidemic prevention data integration platform. The key concept is the data stream pipeline in the platform and the interface of the back-end analysis module to ensure that the platform can meet the needs of various public health requirements.
In addition to integrating various environmental information, including online news and public health announcement systems, we also collect information through the chatbot we developed. We have developed the core of information extraction through this information. The key NLP technology allows important information to be exactly extracted and distinguished. In the quick screening of public health, people can follow the questions on the line bot to understand whether their condition requires immediate medical attention. The system also integrates and summarizes daily public health information for the public. Through participating in the CES2019 exhibition, our public health smart system has also attracted the attention of many manufacturers, including from Nigeria, Africa. In this process, we also understand that different fields and different data sources will have quite different requirements from the bottom infrastructure of the Internet of Things to the analysis and decision-making applications.
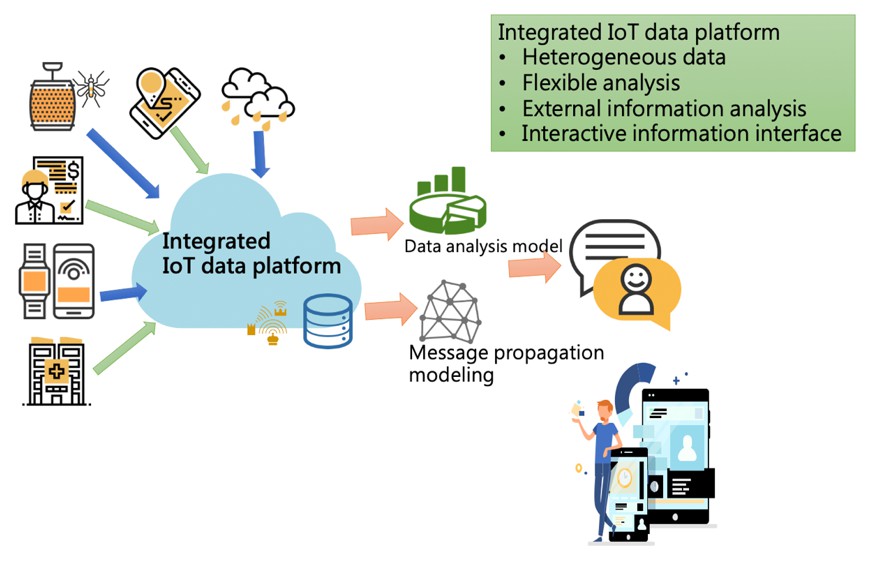
Figure 2: Heterogeneous medical and epidemic prevention data integration and analysis platform
The usage scenario is shown in the Figure 3. For the COVID-19 epidemic, we can integrate with the relevant diagnosis and contact history data of the Department of Health. We can monitor the body temperature of suspected patients in home isolation and report real-time information, which can be used in epidemic control and decision-making. News and information on the Internet are also important resources for judging the spread and influence of the epidemic. Combining the big rich data platform in National Cheng Kung University Hospital, we are continuing to add more information from smart IoT and wearable devices to the platform. Using machine learning and deep learning to predict the progress of patients and the epidemic will be an important foundation and core functions for future smart epidemic prevention platforms.
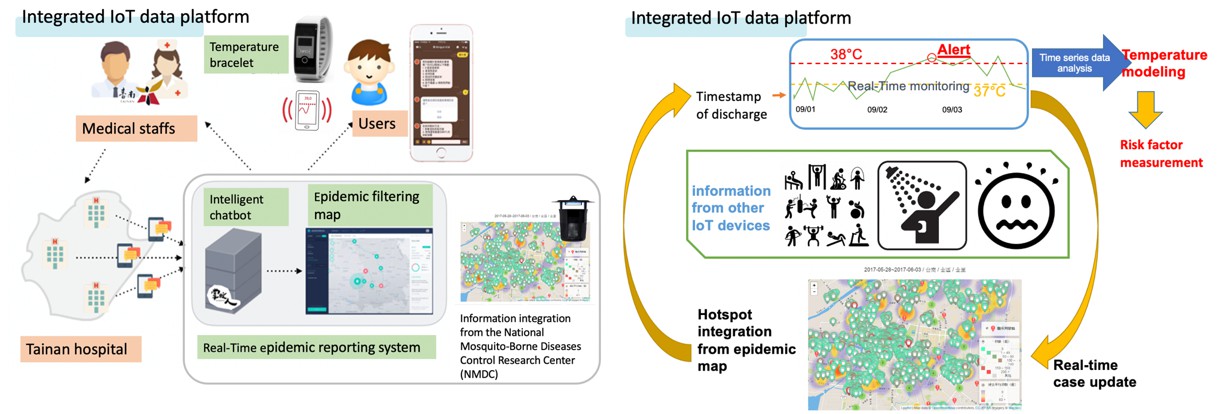
Figure 3: Heterogeneous data integration
STAY CONNECTED. SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER.
Add your information below to receive daily updates.




