An AI-based Pneumonia Detection Platform for COVID-19: MedCheX
Author(s)
Nai-Ying KoBiography
Nai-Ying Ko, RN, PhD is currently director and a distinguished professor of the Department of Nursing in National Cheng Kung University. Her clinical research specializations include health behavior and health disparities with special emphasis on vulnerable populations affected by HIV/AIDS. She serves on the editorial boards of many journals and is author, or coauthor, of more than 150 scientific publications, including several textbooks. Dr. Ko is the pioneer who initiated the HIV counseling and testing programs in Taiwan and created the models of HIV case management in HIV designated hospitals. Those programs and models later became National policy in HIV care in Taiwan. Dr. Ko serves as one of the key advisors to the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan Center of Disease Control and Ministry of Education on HIV/AIDS issues. Dr. Ko has delivered major lectures to health professionals in HIV care in China, Kenya, and Myanmar, and is the recipient of numerous awards. Dr. Ko is truly an example of a nurse educator, researcher, and HIV activist, passionate about caring and advocating for patients with HIV and their families affected by the disease.
Academy/University/Organization
National Cheng Kung Universtiy-
TAGS
-
Share this article
You are free to share this article under the Attribution 4.0 International license
- ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGIES
- Text & Image
- June 21,2020
The incidence and prevalence of emerging infectious diseases have increased with globalization and the universality of transportation, causing a great negative impact on people's health, life, and economy. On January 7, 2020, China detected a new coronavirus that caused Wuhan pneumonia. The World Health Organization (WHO) renamed it "COVID-19" as an emerging infectious disease, which was recognized as an international public health emergency and a pandemic. Variations of body temperatures and heart rates are important indicators of infectious diseases and poor prognosis. Continuous monitoring of variations of body temperatures and heart rates through the portable device can be used as indicators to predict potential cases. The National Cheng Kung University (NCKU) research team and technology manufacturers jointly developed HEARThermo, an innovative wearable device for continuous monitoring of body surface temperature and heart rate, and its cloud-based service platform to early identify the fever and discomfort of the individual in real-time. The NCKU interdisciplinary research team is still working hard on optimization of the Internet of Things system for the prevention of infectious diseases, and the ultimate goal is to reduce the cost of medical care, utilize medical resources, and improve the user's quality of life.

The incidence and prevalence of emerging infectious diseases have increased with globalization and the universality of transportation, causing a great negative impact on people's health, life, and economy. Recently, the novel coronavirus COVID-19 has become a worldwide pandemic. Many research institutes, academia, and the private sector are contributing to prevention efforts. Variations of body temperature and heart rate are important indicators of infectious diseases and poor prognosis. Continuous monitoring of variations of body temperature and heart rate through the portable device can be used as indicators to predict potential cases. However, continuous body temperature monitoring has been limited to intensive care units (ICU) due to the required high staff-to-patient ratios and cumbersome equipment, and might not be applicable for the general population. To date, wearable devices with the advantage of minimizing discomfort and interference with normal human activities have attracted attention in the field of continuous monitoring of body temperature.
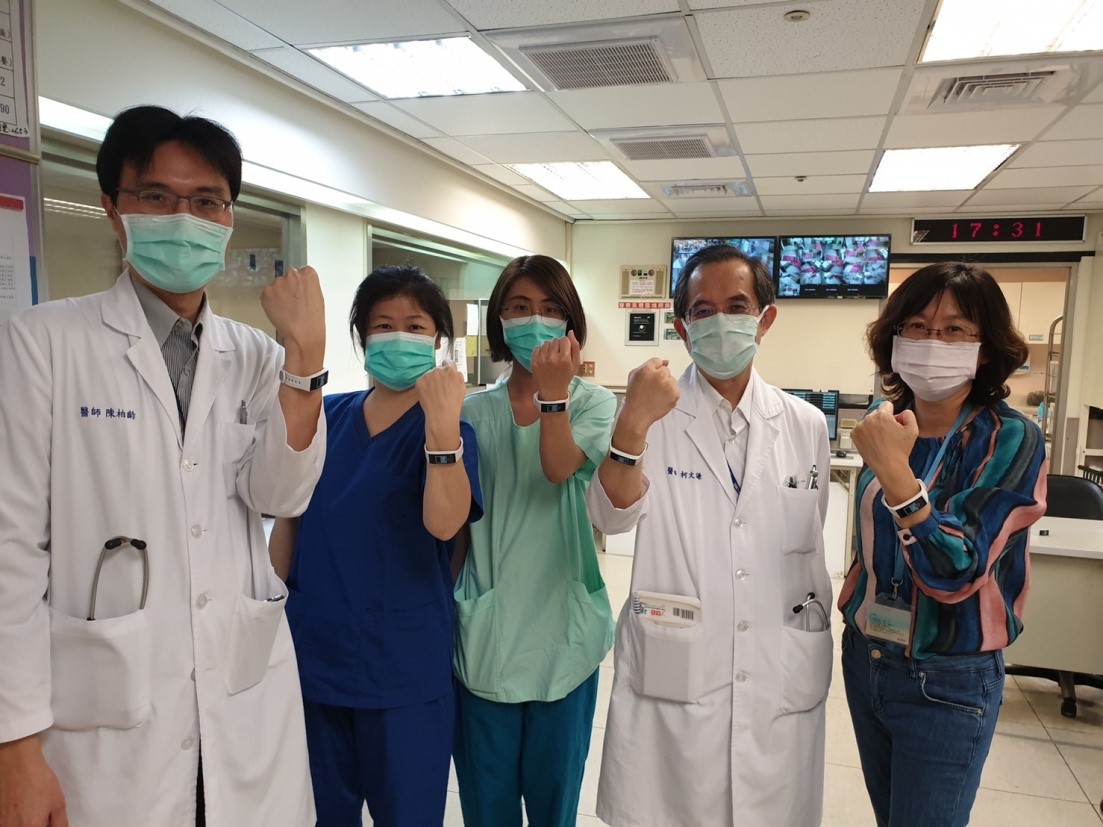
The National Cheng Kung University (NCKU) research team and technology manufacturers jointly developed HEARThermo, an innovative wearable device for continuous monitoring of body surface temperature and heart rate, and its cloud-based service platform to early identify the fever and discomfort of individual in real-time. The wristband embedded biosensors were designed to analyze physiological parameters including body temperature and heart rate variation. These analyzed parameters were used to develop services on prevention and control for infectious disease. Since the beginning of the COVID-19 epidemic, the NCKU research team has entered the frontline field by providing frontline medical and epidemic prevention with a practical reference through scientific research results. HEARThermo was used to continually monitor the body surface temperatures and heart rates of patients, health care providers and people in the community. Through specific AI algorithm analysis, it could be used to detect abnormalities and provide timely care for people with risks. In the COVID-19 epidemic, the NCKU research team provided the HEARThermo to continuously monitor body surface temperature and heart rate to trigger reminders sent by chatbots. The warning messages reminded further measurements by ear thermometers.
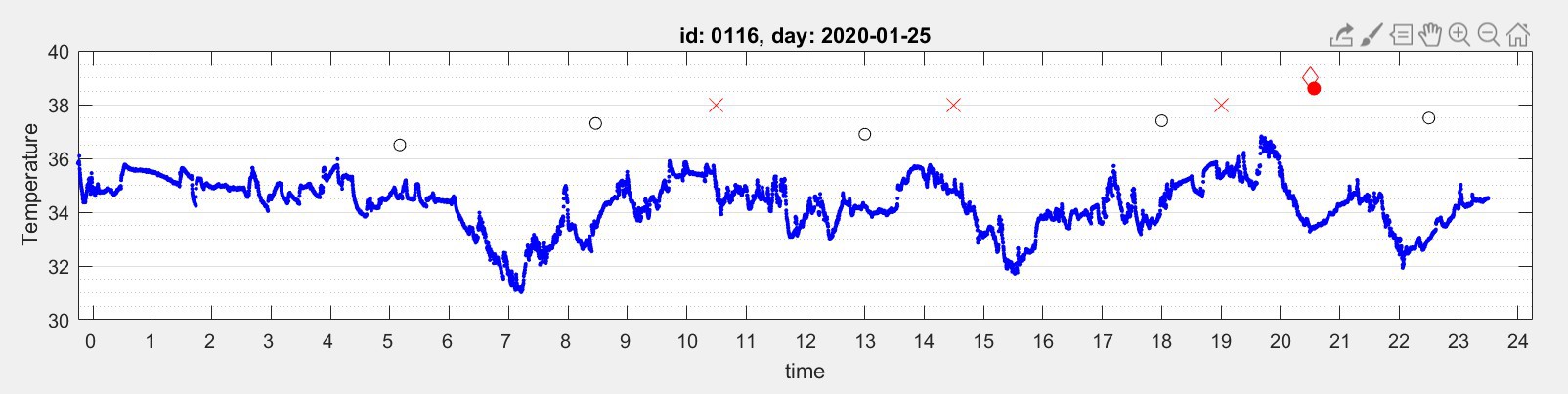
At present, there are more than 430 patients and first-line healthcare providers using HEARThermo and its cloud-based temperature analytics services and platform, and we have received positive feedback from the users and those in the fields. In addition, the scientific findings from the NCKU research team have also been accepted for publication by the Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection. The study findings showed that HEARThermo, as a wearable physiological monitor for remotely monitoring the health status of people under risk of infection, provides real-time data and decision support for healthcare providers and public health agencies. The NCKU research team suggests the application of the innovative wearable device in continuous monitoring of body temperature with heart rate variation may be a solution in the provision of early detection and point-of-care for suspected cases, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The NCKU interdisciplinary research team is still working hard on optimization of the Internet of Things system for the prevention of infectious diseases, and their ultimate goal is to reduce the cost of medical care and utilization of medical resources, and to improve the user's quality of life.
STAY CONNECTED. SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER.
Add your information below to receive daily updates.




