Austronesian Connection Between Taiwan and Indonesia

Author(s)
Gwo-Jen HwangBiography
Dr. Gwo-Jen Hwang is currently a Chair Professor at the National Taiwan University of Science and Technology. He has received many research awards. In 2016, he was announced by Times Higher Education as the most prolific and cited researcher in the world in the field of social sciences.
Academy/University/Organization
National Taiwan University-
TAGS
-
Share this article
You are free to share this article under the Attribution 4.0 International license
- HUMANITIES & SOCIAL SCIENCES
- Text & Image
- November 22,2019
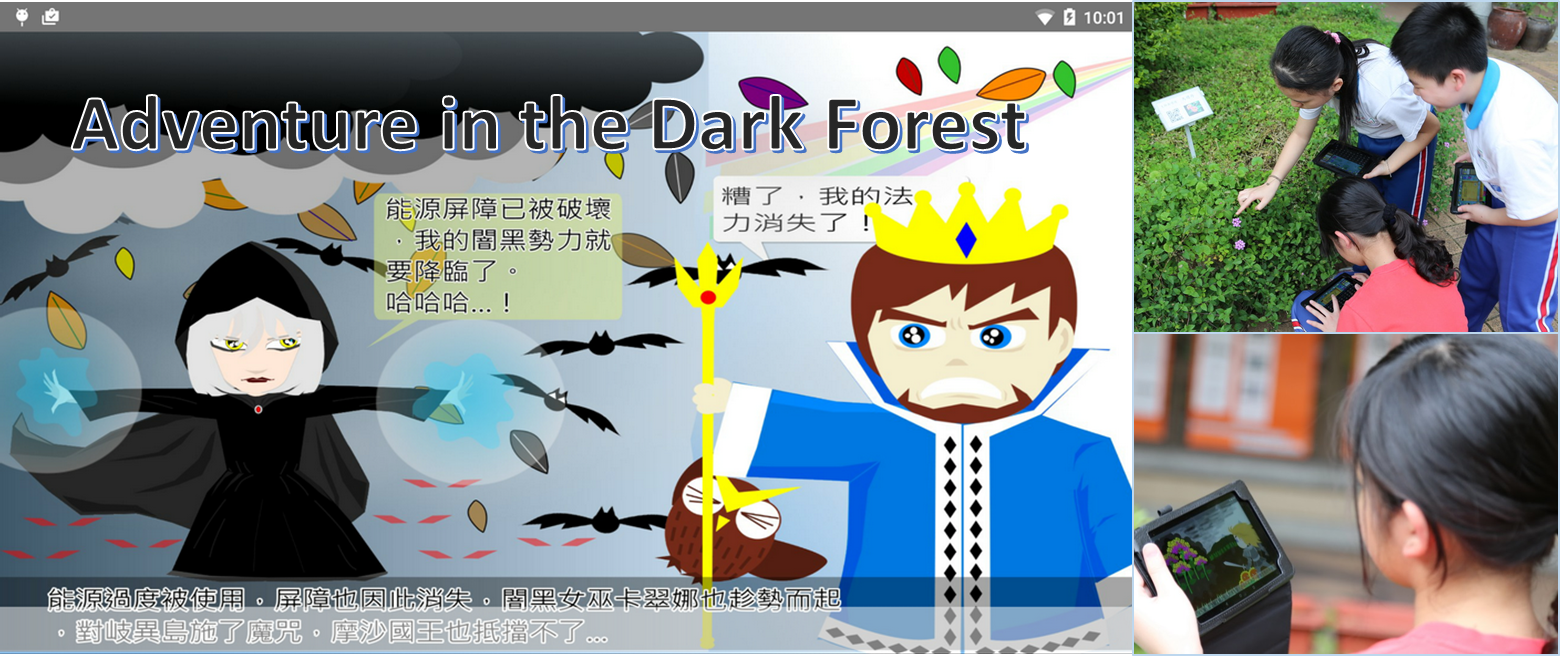
In this project, an inquiry-based collaborative gaming environment was developed to enable students to learn in the real-world environment. The gaming content is associated with the real-world learning targets, such as the plants on the school campus, with a background story to help students learn in an enjoyable manner via playing the game in small teams. During the gaming process, students need to identify the questions raised by the gaming system, make observations and collect data in the real world, discuss with team members, and submit their answers after reaching an agreement on the conclusion. From the practical application in an elementary school, it was found that the real-world gaming approach is able to improve students’ learning achievements, motivation, critical thinking and problem-solving performances. Moreover, the students showed more smart learning behaviors, such as making comparisons and questioning peers’ answers, in the game-based learning contexts.
Engaging students in real-world inquiry and knowledge construction activities can help them link the knowledge learning from textbooks to real-world contexts. Such an approach not only enables students to learn in a meaningful way, but can also foster their competences of solving real-world problems.
Recently, owing to the rapid advancements in mobile and wireless network technologies, educators have started to make attempts to use these technologies in educational settings to promote students’ learning effectiveness. Several scholars have reported that mobile technology-supported learning not only enables students to learn without being limited by time and space, but also provides opportunities to learn and solve problems in real-world contexts. In the meantime, digital game-based learning (DGBL) is considered by scholars as a good approach for increasing students’ motivation and engagement.
In this project, the mobile and network technologies are adopted for implementing the inquiry-based collaborative game associated with the real-world learning targets. The background story of the game is about what happens in a dark forest, which has been cursed by a bad witch. The people living in the forest are waiting for a team of heroes to save them; the learners play the role of the heroes in the game. The aim of this project is to help students to learn in an enjoyable and efficient way to acquire knowledge and solve problems in the real-world contexts as well as using the knowledge they have learned from the textbooks.
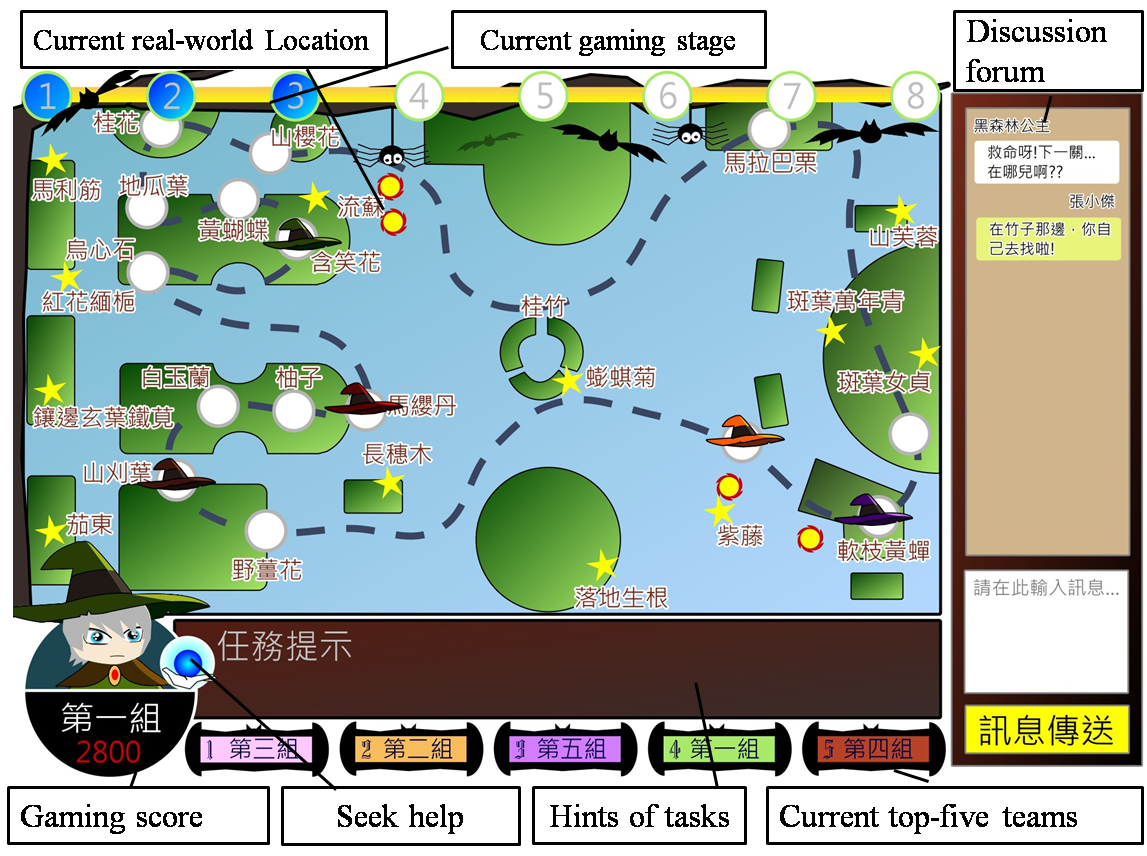
To test the effectiveness of this idea, the implemented inquiry-based gaming system has been applied to a real-world inquiry activity for the elementary school “biology and environmental science” course unit. As shown in the following figure, the map in the gaming interface reflects the physical locations of real-world learning targets (i.e., plants to be observed) on an elementary school campus.


STAY CONNECTED. SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER.
Add your information below to receive daily updates.




