Social Trading – The Next Big FinTech Trend

Author(s)
Chen-Fu ChienBiography
Dr. Chen-Fu Chien is Tsinghua Chair Prof. & Micron Chair Prof. at IEEM Departement, National Tsing Hua University (NTHU). He is the Director of AI for Intelligent Manufacturing Systems (AIMS) Research Center and the Convener of Industrial Engineering and Management Program, Ministry of Science & Technology (MOST).
Academy/University/Organization
National Tsing Hua UniversityEdited by
MOST Artificial Intelligence for Intelligent Manufacturing Systems (AIMS) Research Center, National Tsing Hua University (NTHU)-
TAGS
-
Share this article
You are free to share this article under the Attribution 4.0 International license
- ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGIES
- Text & Image
- February 26,2019
Leading nations including Germany and the USA have reemphasized manufacturing and proposed national strategies such as Industry 4.0 and AMP; China is also promoting Made in China 2025 to upgrade her industrial structure. The paradigm of global manufacturing is changing, and the increasing adoption of AI, big data analytics, cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT), intelligent machines and robotics has empowered manufacturing intelligence for smart production and agile supply chains.
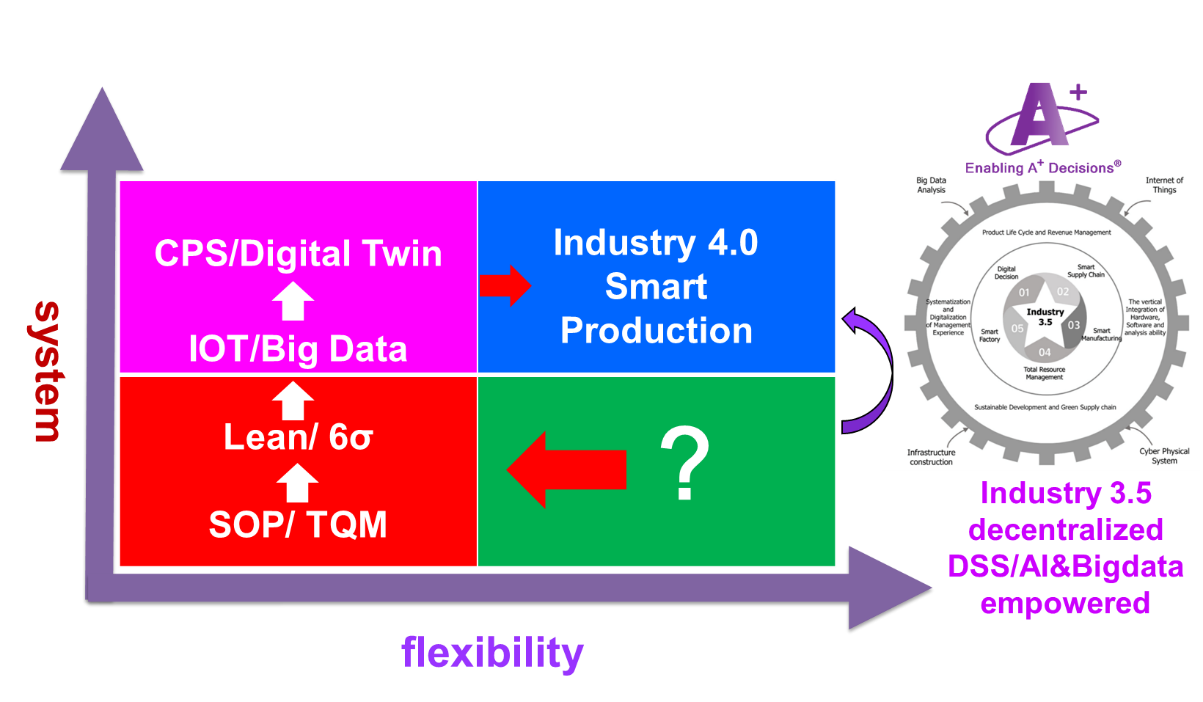
The industry structure of most emerging countries might not be ready for the migration of Industry 4.0, or for facing other challenges such as governing, promoting productivity, maintaining economic growth and creating jobs. Therefore, the AI for Intelligent Manufacturing Systems (AIMS) Research Center, one of the MOST AI centers, aims to integrate various efforts to empower intelligent manufacturing and digital transformation for Made in Taiwan to maintain its competitive advantages. The teams have proposed Industry 3.5 as a hybrid strategy between Industry 3.0 and the to-be Industry 4.0. They have developed core technologies which have validated the approaches through a number of in-depth industrial collaborations with leading companies in different fields including the high-tech manufacturing, assembly, process, and textile industries. With the innovative solutions AIMS has developed, Taiwan is able to play a leadership role in the new manufacturing paradigm of Industry 3.5 and share our experiences with other emergent countries (such as ASEAN countries) facing similar issues.
Leading nations including Germany and the USA have reemphasized manufacturing and proposed national strategies such as Industry 4.0 and AMP; China is also promoting Made in China 2025 to upgrade her industrial structure. The paradigm of global manufacturing is changing, and the increasing adoption of AI, big data analytics, cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT), intelligent machines and robotics has empowered manufacturing intelligence for smart production and agile supply chains.
Today, many leading international companies are competing for the dominant positions in this newly created area through providing novel value-proposition solutions, and/or employing new technologies to construct manufacturing platforms to attract and recruit potential partners and users. But, the industry structure of most emerging countries might not be ready for the migration of Industry 4.0, or for facing other challenges such as governing, promoting productivity, maintaining economic growth and creating jobs.
Therefore, the AI for Intelligent Manufacturing Systems (AIMS) Research Center, one of the MOST AI centers, aims to integrate various efforts to empower intelligent manufacturing and digital transformation for Made in Taiwan to maintain its competitive advantages. The teams have proposed Industry 3.5 as a hybrid strategy between Industry 3.0 and the to-be Industry 4.0. They have developed core technologies which have validated the approaches through a number of in-depth industrial collaborations with leading companies in different fields including the high-tech manufacturing, assembly, process, and textile industries.
First, to make plans for smart manufacturing, the teams have developed the UNISON Decision Framework and PDCCCR which enable coordination of manufacturing strategic decisions including pricing, demand planning, capacity configuration, capital expenditure, and cost structuring to optimize revenue and profitability.
Second, the teams have conducted a series of studies to develop big data analytics solutions which extract effective manufacturing intelligence for yield management in the most complex semiconductor manufacturing processes. For example, there is a study (Kuo, Chien, & Chen, IEEE TASE 2011) based on the manufacturing system and queuing theory to clarify the influence relationship of each input factor, and then to apply the applicant's research on data processing capability of semiconductor manufacturing big data to develop a neural network enabling manufacturing intelligence. Since the important parameters are difficult to obtain, to support the decision making and find out the production decision rules for the most suitable parameter interval to reduce the production cycle time, the research provided specific improvement direction to reduce the in-process standard of each stage of the production line, effectively reducing the production cycle time. This study won the 2011 best paper award of IEEE TASE. Furthermore, as wafer fabrication is reaching nano-technology nodes, linewidth is increasingly complicated for semiconductor manufacturing. The teams have developed a novel approach integrating a feed-forward Run-to-Run (R2R) controller and the proposed mini-max regret tool dispatching rule to determine tool affinity to hedge the variation between the photolithography for pattern development and the etching process to effectively reduce the etching bias caused by tool misalignment.
Third, to enhance flexible decision making for agile manufacturing, the teams have developed resource optimization solutions in light of multiple objectives, and also considering uncertainty and real dynamic settings. For example, they have developed novel algorithms based on genetic algorithms for wafer fabrication scheduling for a leading company. Partial results have been published and won the 2015 best paper of IEEE TSM. Furthermore, focusing on the realistic needs of a TFT-LCD manufacturing company in Taiwan, the teams have developed a smart daily planning and scheduling system to improve the existing manufacturing system to support flexible decision making and agile production without a fully automated environment. Further studies have been conducted to employ the developed core competence based on empirical studies in high-tech manufacturing to other industry segments to support them. Thus, we have also derived critical insights from cross-validation of developed solutions in various settings and have thus constructed solid fundamentals for advanced research.
Through in-depth collaborations with different companies and ongoing studies, the teams also derive insights as the third party observing alternative ways of different organizations to address the needs for intelligent manufacturing. The teams also promote corporate digital transformation to lead small-medium business to proactively participate in the ongoing industrial revolution. With the innovative solutions AIMS has developed, Taiwan is able to play a leadership role in the new manufacturing paradigm of Industry 3.5 and share our experiences with other emergent countries (such as ASEAN countries) facing similar issues.
STAY CONNECTED. SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER.
Add your information below to receive daily updates.




