Earthquake-Related Issues: New Challenges for Offshore Wind Energy

Author(s)
Tzuu-Hseng S. LiBiography
Prof. Li received the Outstanding Research Award in 2017 from the MOST. He is currently a Co-Editor-in-Chief of iRobotics, and Associate Editors of the International Journal of Fuzzy Systems and the IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics. He was the Presidents of the CACS (2008-2011) and of the RST (2012-2015).
Academy/University/Organization
National Cheng Kung UniversitySource
1. C.-Y. Liu, C.-L. Lee, J.-J. Liang, C.-Y. Chen, and T.-H. S. Li*, “Design and Implementation of SLAM by Piecewise Linear Feature Based RBPF for Service Robots,” iRobotics, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 44-54, Dec. 2018. (Hard copy only) 2. Demo videos for Macronix Golden Silicon Awards. 3. C.-Y. Liu, J.-J. Liang, T.-H. S. Li*, and K.-C. Chang, “Motion Imitation and Augmentation System for a Six Degrees of Freedom Dual-Arm Robot,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 153986-153998, Nov. 2019. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8879479-
TAGS
-
Share this article
You are free to share this article under the Attribution 4.0 International license
- ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGIES
- Text & Image; Video
- December 20,2019
Robots that serve us in our daily lives have become a promising trend. In this article, we present our AI-based service robots for shopping in a hypermarket, serving in a beer bar, and working in an office. These service robots are equipped with a RGB-D camera, a microphone array, a SICK laser range finder, speakers, and a notebook. They possess one or two arms, a human machine interface (HMI) system, and a four-wheel independent steering and four-wheel independent driving (4WIS4WID) moving platform, where the omnidirectional movements are their basic function. Three kinds of service robots are introduced: L’ami for shopping in a supermarket, Bob for serving at a beer bar, and May for working in an office. These robots have a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) system and can navigate in a complex environment, avoid obstacles, and grab the desired objects. The robot L’ami can accompany customers and help them to take the products from the shelf. He also has motion planning and path planning capability to optimize the moving distance during the tasks and can grasp every object accurately and autonomously. The bartender, Bob, can talk with you, serve you beer and teach you how to drink whisky. The service robot, May, has two arms and a motion imitation and augmentation system, which allows her to mimic anthropomorphic dual-arm motions and to analogize an imitated motion to different situations. She can carry different sizes of boxes and prepare meeting tasks in an office.
Using robots to replace some manpower is a traditional and outdated way of thinking. Applying service robots to serve us in our daily life is in fact a promising trend in the near future. Some recent results of our AI-based service robots are reported in this article, which includes three parts. In Part I, we will present a paper published in iRobotics and the corresponding result, which received the Diamond Medal of 2017 Macronix Golden Silicon Awards, titled “Design and Implementation of Prototype Service Robot for Shopping.” Part II gives the videos of the experimental results of the Intelligent Bartender Service Robot, which received the Honorable Mention of the 2019 Macronix Golden Silicon Awards. Part III addresses our paper entitled “Motion Imitation and Augmentation System for a Six Degrees of Freedom Dual-Arm Robot” published in IEEE Access and its corresponding videos.
Robots nowadays have increasing chances to interact with people and provide personal services. How to interact with a person and provide suitable services quickly and suitably is not an easy problem. The robot must be equipped with some level of autonomous learning abilities to interact with people and the environment. Mobility is the basis of an interacting robot, because it allows the robot to move in the surroundings. The mobility contains two technologies, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) and path planning. Therefore, we propose a Rao-Blackwellised particle filter (RBPF) based SLAM system. The proposed SLAM system allows the robot to construct the environment map and to localize itself before or while providing personal services. Besides, we also integrated some other functions with the SLAM system to really provide personal services, including path planning, object location establishment, a human robot interaction system, and accompany walking strategy. Therefore, the robot can recognize the person it interacts with, receive commands by the human robot interaction system, establish the location of an object, plan a path, and move to the object.
The intelligent bartender Bob in Part II is our newest service robot and is a brand new outcome of the MOST integrated project entitled “Intelligent Service Robots with Deep Learning Capability for Shopping in a Mega Supermarket.” The system diagram of the AI-based service is shown in Figure 1, where the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) is used to assist with the motion planning process. Some details were submitted for publication but are not introduced here. However, the videos showing that Bob can talk with customers, serve them beer and teach them how to drink whisky are demonstrated.
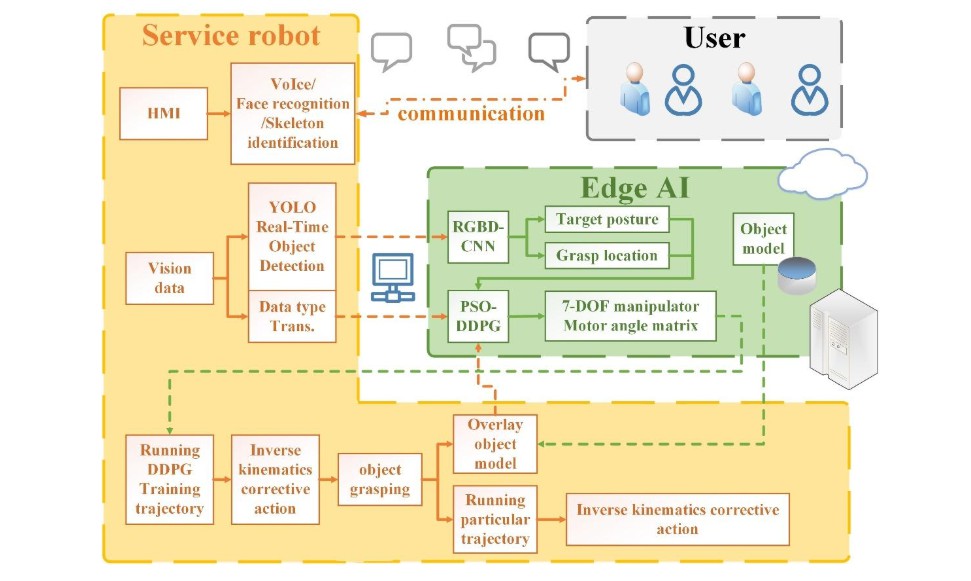
Figure 1. System Diagram of Intelligent Service Robots with Deep Learning Capability.
In Part III, we propose a motion imitation and augmentation system that allows a robot to study a new motion by watching a demonstration performed by a human tutor and to adjust the mimicked motion to cope with the real situations. This implies that a human tutor needs to teach the robot only once, and the service robot will be able to extend the motion to handle different situations. All the real-time experiments have demonstrated the efficiency and feasibility of the proposed system. By using the motion augmentation system, a human tutor can teach a robot a new motion quickly and easily, and the robot can resolve some similar real-life matters autonomously.
STAY CONNECTED. SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER.
Add your information below to receive daily updates.




