Materials Development Towards an Energy-efficient Spintronic Logic Device

Author(s)
Hsuan-Chih Wang & Yuan-Yin ChiewBiography
Hsuan-Chih Wang, PhD., Associate Researcher, Science & Technology Policy Research and Information Center, National Applied Research Laboratories (Corresponding Author, email: hcwang@narlabs.org.tw )
Yuan Yin Chiew, Researcher Assistant, Science & Technology Policy Research and Information Center, National Applied Research Laboratories
Academy/University/Organization
National Applied Research Laboratories-
TAGS
-
Share this article
You are free to share this article under the Attribution 4.0 International license
- ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGIES
- Text & Image
- October 19,2021
The Threat of Information Security is Ubiquitous
Information security is a global issue. Cyber threats can appear in various forms and are therefore unpredictable. Phishing emails, malware, ransomware, viruses, and so on are already a serious issue affecting people’s daily life and the operation of enterprises. According to the Cyber Risk Index (CTI) investigation by TrendMicro and the Ponemon Institute, the global average CRI is 0.42 (where a lower index means a higher risk), and the risks of cyberthreats are higher and still inclining. Take the US as an example; the CRI index has worsened from -0.14 in 2018 to -1.27 in 2021 (TrendMicro, 2021), with serious international network attacks happening in 2020 reflecting the extent to which enterprises can be affected. Travelex, a London-based foreign exchange company, had its operations crippled for weeks due to a ransomware attack. A German hospital and Universal Health Services (UHS), a healthcare provider with over 400 facilities in the US, UK, and Puerto Rico, were hit by ransomware, which broke down its entire IT infrastructure and phone system in the US. The US Government offices were targeted by a series of mega cyberattacks, allegedly related to state-sponsored threat organizations. As the operation of medical care institutions are extremely important to society, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA), the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) released an alert of an increase in ransomware attacks on US hospitals, and emphasized that defense against ransomware attack must be well prepared.
All countries face serious cyber threats, and Taiwan is no exception. According to an information security investigation by iThome 2020, one in every four enterprises (nearly 25.6%) encounter more than 50 information security incidents, and the proportion is rising every year. The high-tech industry, the financial industry, government agencies, and schools are often targeted in these attacks (Lo, 2021). The Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) was attacked by a virus which led to an estimated loss of NT$5.2 billion in 2018, making it the largest information security incident in Taiwan to date. There have been many other ransomware attack cases in recent years, such as the ransomware attack on Compal’s and Hon Hai’s Mexico branches, resulting in production line disruption. Advantech Co., Ltd. was experienced a data leak when attacked by ransomwares. As working and studying patterns have changed rapidly due to the COVID-19 pandemic, cyberattacks have grown sharply. The research by CheckPoint shows that the frequency of cyberattacks in Taiwan in April and May had increased by 17%. (Check Point, 2021).
The Information Security Industry in Taiwan
An investigation done by the Taiwan Information Security Association (TWISA) shows that the information security industry in Taiwan still has a long way to go. There are 324 domestic manufacturers, yet they make up only 21.6% of the domestic market. Among the latest information security technologies are Zero Trust Access and Security Access Service Edge, both of which are used for cloud access services and data operation. The technology of Zero Trust Access (ZTA) is mostly used to verify, authorize, and encrypt in services, especially in an environment where data is opened and shared. The Security Access Service Edge (SASE) is a cloud-based IT model that integrates wide area network (WAN) with network security functions (such as CASG, FWaas and ZTA), delivering them to a single service provider. By using ZTA, threats will not be able to move horizontally within the network, thus reducing risks of information security and disruption. SASE guarantees the security of digitalization and cloud application transformation in enterprises, and is hence the best practice of ZTA for enterprises. In sum, the information security industry helps domestic enterprises act proactively to reduce the incidents of information security in Taiwan, to avoid core information systems and services being attacked, and to reduce the risk of enterprise disruption.
The Policy of Information Security in Taiwan
Apart from the efforts domestic industries are making in response of enterprise operation demands when confronting cyberattack risks, the Taiwan government is also taking approaches from a national overall perspective. The National Information & Communication Security Taskforce of the Executive Yuan is in charge of overall planning to defend against information security threats, implementing a quadrennial program of the Develop Plan of National Information and Communication since 2001. Phases 1 and 2 are about mechanisms, intending to improve the information security infrastructure in Taiwan. Phases 3 to 6 are about development. The 6th phase (2021-2024) lays emphasis on initiative defense, putting effort into talent cultivations of information security to enhance indigenous R&D competency, promoting the cooperation between the public and private sectors to establish a better environment of cyber security, utilizing new technology to actively defend against cyber threats, and developing capabilities of safe IoT in private sectors to enforce Taiwan as a representative information security hub in the Asia-Pacific region. Generally speaking, the policies and programs of information security in Taiwan focus on talent cultivation, R&D, and international impact. The Excellence and Sprout Information Security Program has been implemented to enhance international cooperation and multiple methods of talent cultivation. In terms of R&D capability, the government has launched the Information Security Industry Development Action Plan for a niche market of the Taiwan information security industry with public-private partnerships (PPP). Validation site(s) and test bed(s) are also prepared for local validation so as to make the Taiwan information security industry appealing to the global market of information security.
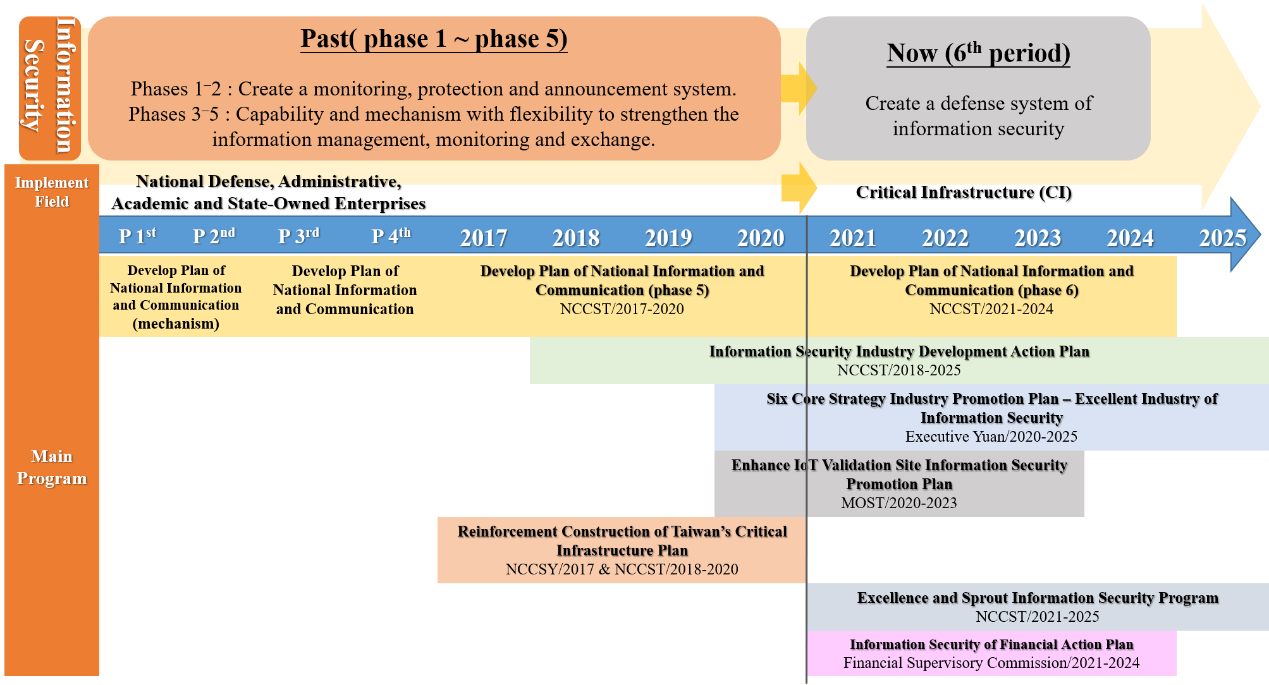
Figure 1. Progress Information Security Program in Taiwan
Source: National Information & Communication Security Taskforce
According to the data retrieved from the Government Research Bulletin (GRB) system created by the Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan from 2014-2020, the investment in information security technology focused primarily on cyber-attack, cyber-defense, mobile and edge device security, IoT security, talent cultivation, and identification and recognition. Identification, mobile and edge device security, and IoT security are the technology elements for ZTA and the SASE model to defend against attacks. Talent cultivation is crucial to fulfill the technology development to set up infrastructures for AIoT. In short, MOST is investing in the technology of active defense systems, talent cultivation, and better AIoT infrastructures for the technology and talent needs of Taiwan’s information security industry. These actions correspond to the strategies of Taiwan’s information security policies aiming to establish Taiwan as a global information security research center.
Conclusion
Protecting information systems from threats is a global issue. Taiwan, an ICT export-dominant country, plays an important role in the global ICT supply chain. Therefore, the enhancement of Taiwan’s information security capabilities not only increases the capability of domestic enterprises to defend against attacks, and promotes exports of Taiwan’s ICT products. In light of this, Taiwan’s government has formulated policies on information security and is dedicated to related research and development. Besides, Taiwan is well-known for its robust semiconductor manufacturing clusters, advanced manufacturing capacity and abundant ICT talents. However, there is still plenty of room for progress in the information security industry. In order to enhance global visibility and the influence of this industry, the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) in Taiwan has launched various funding programs, such as information security S&T research grants, incubation projects for R&D personnel, collaborations in validation sites and test beds, and integration of the information security R&D and services with public-private partnership (PPP) contracts. With those actions, Taiwan’s government wishes to make Taiwan the global information security research and business hub in the future.
Reference:
- Cheng Han, Lo (2021). iThome 2021 Information Security Investigation of Enterprises:Taiwan Cyber Attack in 2020 . iThome. https://www.ithome.com.tw/article/144234
- TrendMicro(2021). Cyber Risk Index. https://www.trendmicro.com/zh_tw/security-intelligence/breaking-news/cyber-risk-index.html
- Check Point. (2021). Cyber Security Report 2021.
STAY CONNECTED. SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER.
Add your information below to receive daily updates.




