Sharing and dynamic accesses of spectrum and heterogeneous radio access networks have been an important area of research on next generation mobile networks. They require innovations between regulatory policy and technology. The research team of the Dynamic Spectrum Access Laboratory (DSA Lab), Graduate Institute of Communications Engineering and Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, has three research objectives:
O1) to help ICT industry grasp technology, system and service developments of shared spectra and RAN accesses;
O2) to provide scientific and technological support and recommendations to both wireless and mobile service operators and regulatory policy-makers; and
O3) to develop foresights about spectrum and RAN sharing technologies and operation model developments.
To achieve these objectives via proof-of-concept (POC) demonstrations and to develop an experiment environment for research, together with other research institutes the research team has designed and implemented the Virtually Shared Spectrum Access (ViSSA) platform. ViSSA 2.0 has seven innovatively designed and integrated parts: i) an observatory for periodic spectrum sensing; ii) a monitoring (Figure 2) and management center of spectrum accesses with a spectrum database; iii) an emulator of incumbent spectrum accesses; iv) LTE small cells of multiple networks of secondary accesses; v) feature-based sensing of incumbent signals; vi) License Assisted Access operation management for fair access with WiFi networks; vii) a simplified spectrum access system of a three-tiered spectrum sharing framework; and viii) intra- and inter- Lab networking. The research team has achieved successful experiments and POC demonstrations of spectrum and RAN sharing over ViSSA 2.0.
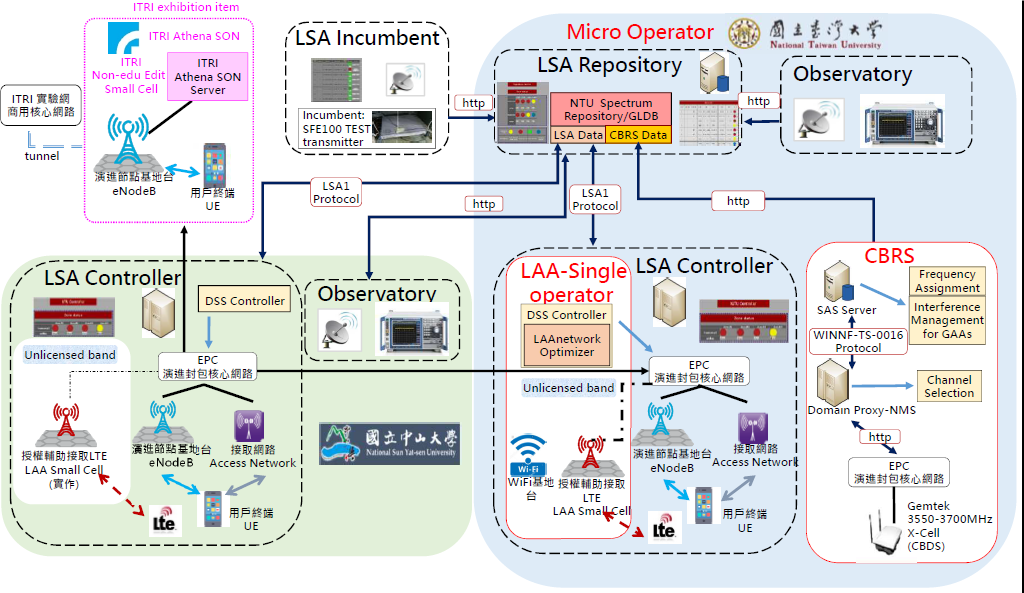
Figure 1: ViSSA 2.0 Platform Architecture
With the emergence of Internet of Things (IoT) and the rapid development of wireless broadband access (WBA) technologies and penetration of mobile devices, worldwide forecasts expect 1000 or more-fold traffic growth in mobile and wireless data traffic in the coming five to ten years. Besides traffic volume, wireless and mobile accesses will accelerate in terms of quality requirements and service diversity. WBA service providers need to acquire many more spectrum bands than the currently available ones, and deploy a large amount of network infrastructure. How to effectively keep up with the trend of much higher throughput, much lower latency, and greater mobility range than the current ones with limited spectrum resources among heterogeneous networks has brought many new opportunities and challenges.
Sharing and dynamic accesses of spectrum and heterogeneous RANs have been an important area of research on next generation mobile networks. There are many questions to be answered by further research, experiment and demonstration regarding technologies, architectures, operation models, and regulatory policies. It requires innovations between regulatory policy and technology. The research team of the Dynamic Spectrum Access Laboratory (DSA Lab), Graduate Institute of Communications Engineering and Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University, has been conducting research in this area since 2014 through projects supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Institute for Information Industry and Telecom Technology Center. The research objectives of the DSA Lab are as follows:
O1) to help the ICT industry grasp technology, system and service developments of shared spectrum and RAN accesses;
O2) to provide scientific and technological support and recommendations to both wireless and mobile service operators and regulatory policy-makers; and
O3) to develop foresights about spectrum and RAN sharing technologies and operation model developments.
Specifically, the regulatory framework study has evolved from License-exempt TV White Space (TVWS) to Licensed Shared Access (LSA), Licensed Assisted Access (LAA), and Citizens Broadband Radio Services (CBRS) with three tiers of incumbent, priority access and general authorized access. Technological research topics include the coexistence of heterogeneous networks, channel measurement, interference management, dynamic resource allocation and coordination, and sharing mechanisms and platform design for converged accesses. Specific applications include campus security monitoring systems and wireless accesses among 4G/5G/WiFi for Industrial IoT (IIoT) in smart factories. To achieve these objectives via proof-of-concept (POC) demonstrations and to develop an experiment environment for research, the DSA Lab research team has designed and implemented the Virtually Shared Spectrum Access (ViSSA) platform together with the Mobile Broadband Network Lab, National SunYat-Sen University and Information and Communications Research Laboratories, Industrial Technology Research Institute, and the Radio Spectrum Lab, Telecom Technology Center.
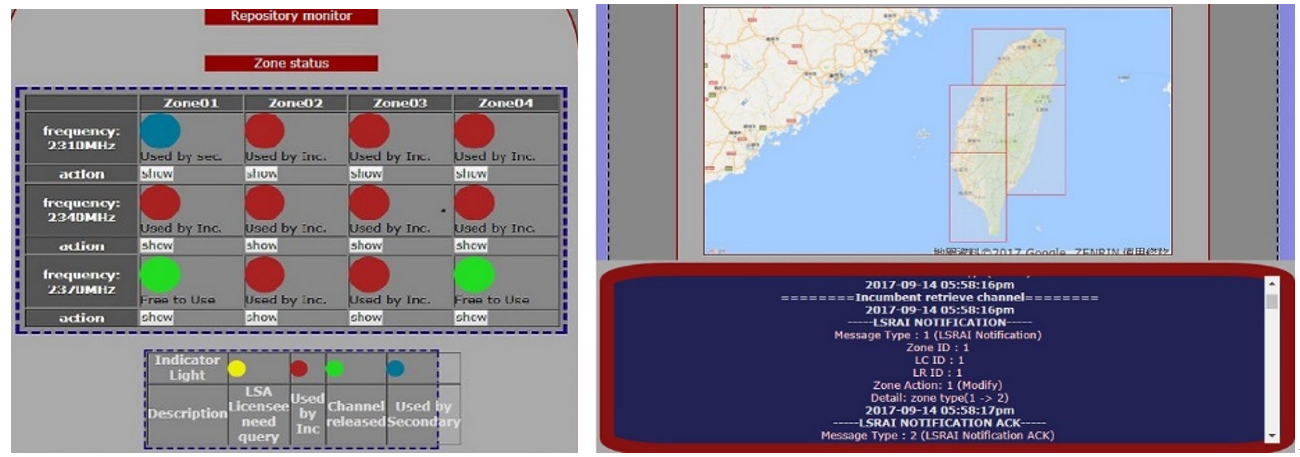 Figure 2: Monitoring and management display
Figure 2: Monitoring and management display
The ViSSA 2.0 platform depicted in Figure 1 innovatively integrates seven parts by combining 4G (LTE) small cells, emulators and management servers:
i) an observatory that periodically senses spectrum accesses and collects data;
ii) a monitoring (Figure 2) and management center of spectrum accesses with a spectrum repository that extends a license-exempt mode compliant geo-location database (GLDB/SR);
iii) incumbents of spectrum accesses emulated by an orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) transmitter that may register to GLDB/SR or directly access its spectrum;
iv) LTE small cells of multiple networks of secondary accesses, each equipped with a controller (Figure 3) to communicate between GLDB/SR and its own network management;
v) feature-based sensing of incumbent signals emulating a Universal Software Radio Peripheral emulator;
vi) LAA operation management with a Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) controller and optimizer for shared access of unlicensed bands with WiFi networks;
vii) a simplified Spectrum Access System (SAS) and domain proxy (DP) of CBRS framework implementing the functions of spectrum assignment, channel selection and interference management;
viii) networking within the DSA lab and among Labs through the Internet.
The research team has applied ViSSA 2.0 to research experiments for design validation and data collection and has performed various proof-of-concept demonstrations of various spectra and RAN sharing designs on ViSSA 2.0. Successful experiments and demonstrations are as follows:
1) TVWS shared accesses: Spectrum access management by registration on the geolocation database for supporting smart grid applications;
2) LSA accesses: feature-based incumbent detection, spectrum repository (SR)-based management, secondary user evacuation from incumbent channels, and secondary user re-activation at another unused channel in an admissible duration of 60 to 70 seconds;
3) CBRS GAA accesses: game theoretic coordination of GAA spectrum accesses by SAS to individual operators; and
4) A double auction mechanism for short interval spectrum sharing.
5) Fair accesses of unlicensed bands between LAA small cells and WiFi APs for supporting smart factory communications in the EU-TW H2020 Clear5G project.



 Figure 2: Monitoring and management display
Figure 2: Monitoring and management display



